- HOME
- ABOUT
- RESEARCH
- INSIGHTS & HAPPENINGS
- JOIN US
- CONTACT US
-

Stroke: sometimes called a brain attack, occurs when something blocks blood supply to part of the brain or when a blood vessel in the brain bursts.
A stroke, also known as a brain attack, happens when the blood supply to a portion of the brain is cut off or when a blood artery in the brain bursts. Parts of the brain are injured or die in either circumstance. A stroke can result in long-term brain damage, disability, or even death.
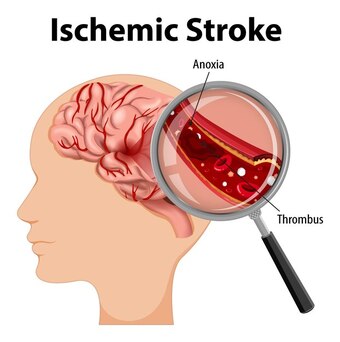
An ischemic stroke happens when the blood supply to a portion of the brain is cut off or decreased, preventing brain tissue from receiving oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells start to die within minutes. A stroke is a medical emergency that must be treated as soon as possible. Early intervention can help to prevent brain damage and other consequences.
If you suspect that you or someone you’re with is having a stroke, pay close attention to when the symptoms began. Some treatment options are most effective when administered soon after the onset of a stroke.
Signs and symptoms of stroke include:
They were experience confusion, slur words or have difficulty understanding speech.
They were develop sudden numbness, weakness or paralysis in the face, arm or leg. This often affects just one side of the body. Try to raise both your arms over your head at the same time. If one arm begins to fall, you may be having a stroke. Also, one side of your mouth may droop when you try to smile.
They were suddenly have blurred or blackened vision in one or both eyes, or you may see double.
A sudden, severe headache, which may be accompanied by vomiting, dizziness or altered consciousness, may indicate that you’re having a stroke.
They will stumble or lose your balance. You may also have sudden dizziness or a loss of coordination.

There are two main causes of stroke: a blocked artery (ischemic stroke) or leaking or bursting of a blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke). Some people may have only a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain, known as a transient ischemic attack (TIA), that doesn’t cause lasting symptoms.
Effective treatment of stroke can prevent long-term disability and save lives.
The specific treatments recommended depending on whether a stroke is caused by:
Treatment usually involves taking 1 or more different medicines, although some people may also need surgery.
I) Treating Ischemic strokes
If you have had an ischemic stroke, it is normally suggested that you take a combination of medications to treat the problem and prevent it from happening again. Some of these medications must be taken immediately and only for a short period, while others must be begun after the stroke has been treated and must be used long-term.
Ischaemic strokes are frequently treated with injections of alteplase, a medication that breaks blood clots and restores blood flow to the brain. This application of “clot-busting” medication is known as thrombolysis. Alteplase is most effective if started as soon as possible after the stroke, preferably within 4.5 hours. It is not generally advised if more than 4.5 hours have passed, as it is unclear how effective it is after this period. Before using alteplase, a brain scan must be performed to confirm the diagnosis of an ischemic stroke. This is because the medication has the potential to exacerbate the bleeding that happens in hemorrhagic strokes.
After an ischemic stroke, most people are given aspirin right away. Aspirin, in addition to being a pain reliever, is an antiplatelet agent, which reduces the probability of another clot developing. Clopidogrel and dipyridamole, among other antiplatelet medications, may be used afterward.
II) Treating Hemorrhagic strokes
Some patients who have had a hemorrhagic stroke, like those who have had ischemic strokes, will be given medication to decrease their blood pressure and avoid further strokes. If you were taking anticoagulants before your stroke, you may also require treatment to reverse the effects of the medication and lower your risk of additional bleeding.
Emergency surgery may be required on rare occasions to remove any blood from the brain and repair any broken blood vessels. This is normally accomplished with the use of a surgical technique known as a craniotomy. A portion of the skull is removed during a craniotomy to provide the surgeon access to the source of the bleeding. The surgeon will repair any damaged blood arteries and check for any blood clots that could restrict blood flow to the brain. After the bleeding has stopped, the bone removed from the skull is generally replaced with an artificial metal plate.
Hydrocephalus, a consequence of hemorrhagic strokes, can potentially be treated surgically. Damage from a stroke causes cerebrospinal fluid to accumulate in the cavities (ventricles) of the brain, causing symptoms such as headaches, nausea, sleepiness, vomiting, and loss of balance. Hydrocephalus can be treated by inserting a tube into the brain called a shunt, which allows the fluid to drain.

CelltiX is a type of extracellular vesicle from Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) manufactured in a cGMP-compliant facility.
It is a novel form of a major paracrine factor released by MSCs into a culture medium, which plays an important role in a wide range of biological processes.
CelltiMax is a product derived from human umbilical cord-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). The cells are cultured, then administered to the patient via intramuscular or intravenous injection. They have the ability to differentiate into specialized cells with specific functions for various parts of the body, and can reduce inflammation, repair, renew, regenerate, and replace damaged cells.
Definition
Stem cells are unspecialized cells of the human body.
Extracellular vesicles, which is the medical term for tiny bubbles that are released from stem cells.
Function
Unique, can become any type of cell, and they act as both building blocks and repair mechanisms in your body.
Carry genetic information and proteins to cells throughout your body, and they create paths for communication between cells.
Origins
Donor stem cells are placed in your body and are guided into becoming specific cells in the body to replace and repair diseased cells.
Exosomes are extracted from donated human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and sterilized.
Growth Factors
Less amount of growth factors compared to exosomes.
Exosomes contain nearly three times the amount of growth factors. More growth factors mean a better ability to restore and revitalize target cells.
Administration
Improve bodies’ natural healing abilities
High stabililty
Modulate the immune system
Low toxicity and immunogenicity
Locate and reduce areas of inflammation
High penetration
Replace damaged and diseased cells
Enhanced delivery efficiency
Cross the endothelial brain barrier.
Enhanced immunity
Migrate to sites of injury.
Improved metabolism.
Encourage existing cells to self-repair.
Reduced repetition.
Immune modulation.
Increased communication ability.
Transform into neurons.
Improvements in verbal skills, writing skills, self-care skills, attention span, and concentration
Promote the formation of nerve cell axons.
Tolerance of different foods.
If you believe that our treatment options may be able to improve your condition and enhance your quality of life, please contact us to schedule a complimentary consultation with one of our in-house clinical specialists. Our consultations are available in both Malay and English language.






Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified cGMP laboratory, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.



Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified cGMP laboratory, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.


Proudly powered by CTG © 2010-2025 Cell Tissue Group, a Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Spin-Off Company. – All Rights Reserved.