- About
- Research
- Product
- Medical Use
- CelltiSS
- HOME
- ABOUT
- RESEARCH
- INSIGHTS & HAPPENINGS
- JOIN US
- CONTACT US
-







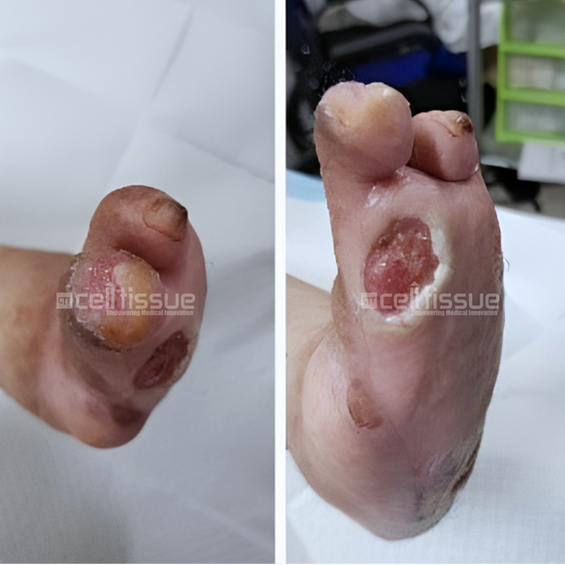
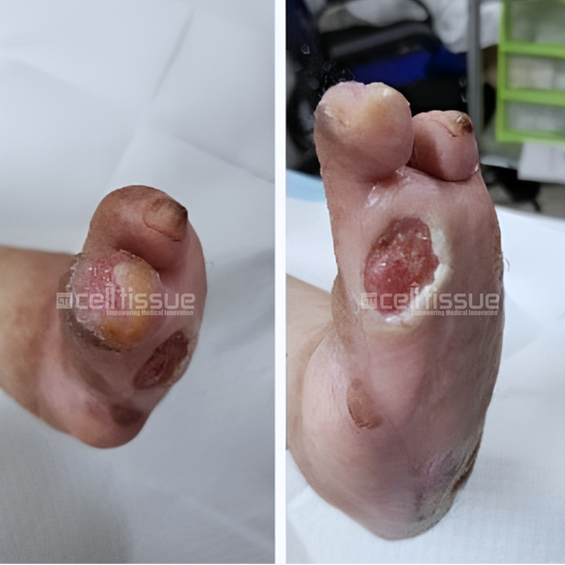
The patient above with diabetes had a wound caused by soft tissue injury. At presentation, the wound was one month old. At the start of the application, there were two wounds located at the base of the left toe, approximately 4 cm2 in size, and one at the tip of the fourth toe, approximately 1 cm2 in size. On day 91, both wounds at the base and tip of the left toe had achieved 100% closure.
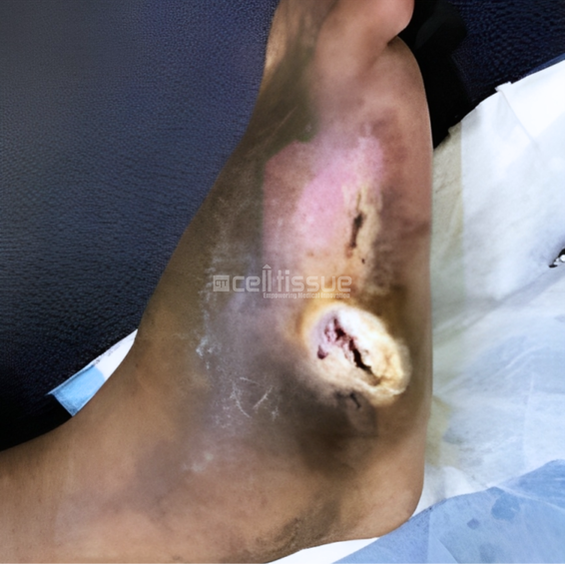
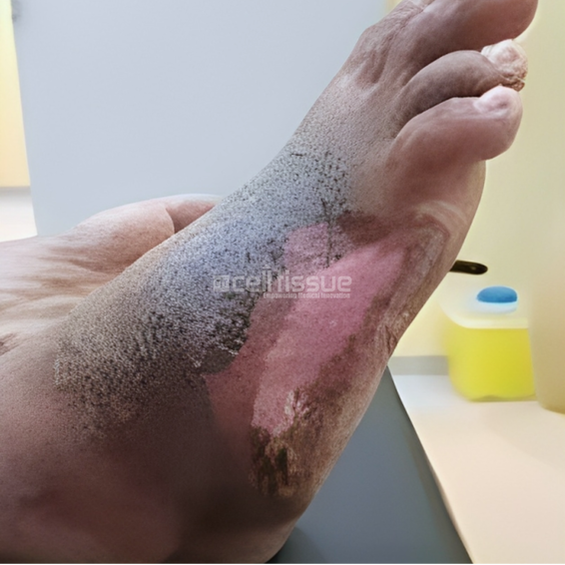
This case involved a 36-year-old male with a diabetic foot ulcer located on the lateral side of the right foot caused by callus removal. At presentation, the wound was two months old and had a size of 9 cm2. On day 73, the wound had completely closed with a mild callus formation on the lateral side of the right foot.

Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified cGMP laboratory, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.



Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified cGMP laboratory, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.


Proudly powered by CTG © 2010-2025 Cell Tissue Group, a Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Spin-Off Company. – All Rights Reserved.