- HOME
- ABOUT
- RESEARCH
- INSIGHTS & HAPPENINGS
- JOIN US
- CONTACT US
-

Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetes causes diabetic retinopathy, which is an eye disease. Diabetes can have an impact on your eye care, making frequent eye exams even more necessary. Vision loss can be caused by damaged blood vessels as well as abnormal new ones.

Diabetes can cause diabetic retinopathy, an eye illness that occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina. These damaged vessels can leak, close off, or form new, abnormal vessels, which can lead to vision loss.
It is crucial for people with diabetes to have regular, comprehensive eye exams, at least once a year, to detect diabetic retinopathy early. As diabetic retinopathy often has no early symptoms, early detection is key to preserving vision.
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, there are usually no symptoms. Some people notice changes in their eyesight, such as difficulty reading or seeing distant objects. These modifications may come and go. Blood vessels in the retina begin to bleed into the vitreous in the later stages of the disease (the gel-like fluid that fills your eye). If this occurs, you may notice dark, floating spots or streaks that resemble cobwebs. Sometimes the spots go away on their own, but it’s critical to seek treatment right away. Scars at the rear of the eye can occur if not treated. Blood vessels may begin to bleed again, or the bleeding may worsen.
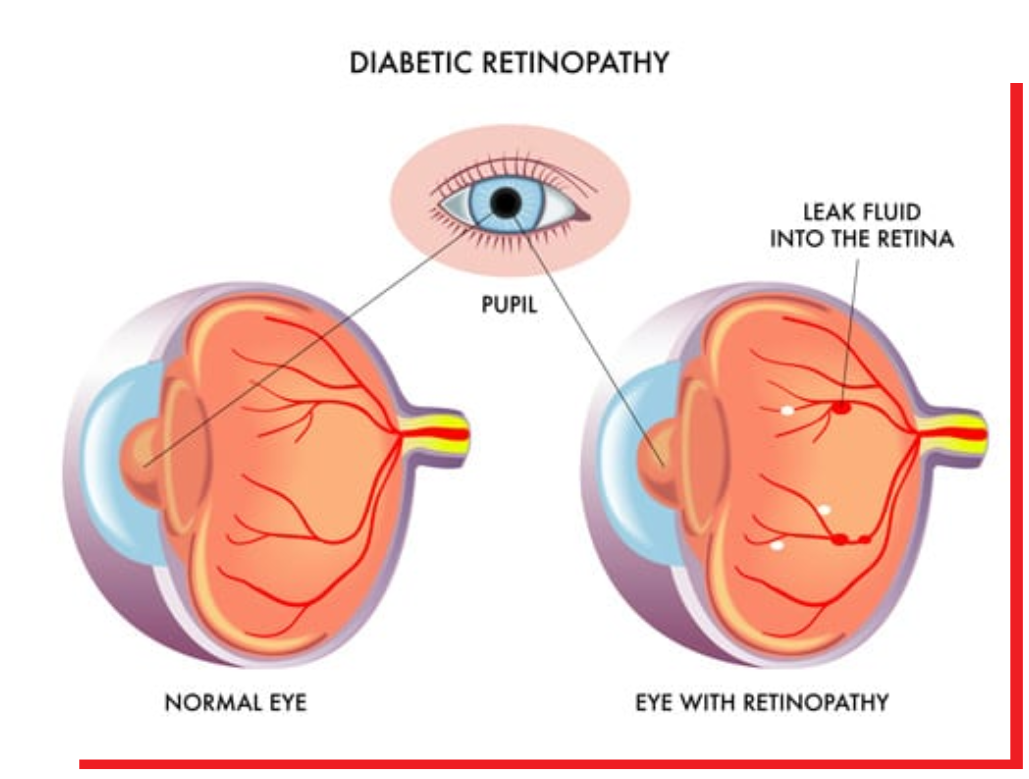
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by elevated blood sugar levels associated with diabetes. High levels of sugar in the bloodstream can damage the retina over time. The retina is the part of the eye that detects light and sends visual information to the brain via the optic nerve.
Diabetes also causes damage to blood vessels throughout the body. In the eyes, sugar clogs the tiny blood vessels that lead to the retina, causing them to leak fluid or bleed. As a result, the eyes grow new blood vessels that are weak and easily leak or bleed which can lead to vision loss if left untreated.
Your eye doctor will probably only keep track of how your eyes are doing in the early stages of diabetic retinopathy. Some diabetic retinopathy patients may require a complete dilated eye exam every 2 to 4 months. It is critical to begin treatment as soon as possible in the later stages, especially if you experience alterations in your eyesight. While treatment will not restore your vision, it will prevent it from deteriorating. It’s also critical to managing your diabetes, blood pressure, and cholesterol.
I) Injections:
Medicines called anti-VEGF drugs can slow down or reverse diabetic retinopathy. Other medicines, called corticosteroids, can also help.
II) Laser treatment:
To reduce swelling in your retina, eye doctors can use lasers to make the blood vessels shrink and stop leaking.
III) Eye surgery:
If your retina is bleeding a lot or you have a lot of scars in your eye, your eye doctor may recommend a type of surgery called a vitrectomy.
CelltiX is a type of extracellular vesicle from Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) manufactured in a cGMP-compliant facility. It is a novel form of a major paracrine factor released by MSCs into a culture medium, which plays an important role in a wide range of biological processes.
CelltiMax is a product derived from human umbilical cord-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). The cells are cultured, then administered to the patient via intramuscular or intravenous injection.
The cells have low immunogenicity making them safe, well-tolerated and free of side effects. They have the ability to differentiate into specialized cells with specific functions for various parts of the body, and can reduce inflammation, repair, renew, regenerate, and replace damaged cells.
Definition
Stem cells are unspecialized cells of the human body.
Extracellular vesicles, which is the medical term for tiny bubbles that are released from stem cells.
Function
Unique, can become any type of cell, and they act as both building blocks and repair mechanisms in your body.
Carry genetic information and proteins to cells throughout your body, and they create paths for communication between cells.
Origins
Donor stem cells are placed in your body and are guided into becoming specific cells in the body to replace and repair diseased cells.
Exosomes are extracted from donated human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and sterilized.
Growth Factors
Less amount of growth factors compared to exosomes.
Exosomes contain nearly three times the amount of growth factors. More growth factors mean a better ability to restore and revitalize target cells.
Administration
Accelerates healing.
Reduced inflammation
Eliminates pain and inflammation
Supports metabolic function
Enhances collagen production
Improves brain health
Decrease nerve damage
Reduces chronic pain
Less invasive procedure
Enhances tissue regeneration
Less invasive procedure
Boost immune health

If you feel we might be able to offer meaningful improvement to both your condition and your quality of life, then please reach out to schedule a free consultation with one of our in-house clinical experts. We offer consultations in both Malay and English.





Review your medical history & recent evaluations
Explore what your treatment package might look like
Answer any questions you have about us
Answer any questions you have about the therapies
Discuss practical next steps,
if you feel we can effectively treat you

Established in 2010, Cell Tissue is a Malaysian advanced medical technologybased company, a spin-off of the National University of Malaysia (UKM), one of the country’s leading universities and research institutes.
Cell Tissue is known as Malaysia’s FIRST Tissue Engineering Firm, awarded by the prestigious Malaysian Book of Records in 2016, operated in a certified Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) laboratory following PIC/S standards by the National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA), a division of the Ministry of Health Malaysia.


Proudly powered by CTTSB © 2010-2024 Cell Tissue Technology Sdn Bhd, a Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia spin-off Company. – All rights reserved.