- HOME
- ABOUT
- RESEARCH
- INSIGHTS & HAPPENINGS
- JOIN US
- CONTACT US
-

Pituitary disorders: Pituitary problems typically result from the pituitary gland being either overactive or underactive.
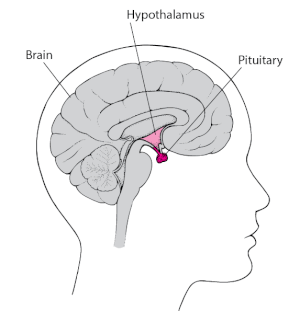
The pituitary gland, which is about the size of a pea, is located near the base of the brain, behind the bridge of your nose. The hypothalamus, a different region of the brain, is located not far from the pituitary gland.
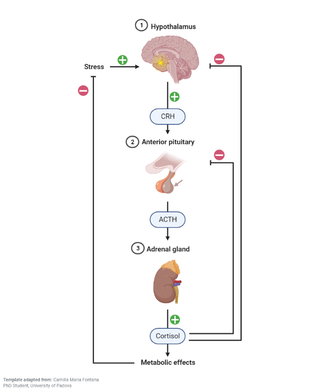
The human body has systems that constantly monitor changes and other vital functions. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus are a part of some of these systems.
The hypothalamus regulates bodily functioning by receiving information from a variety of sources. One of the ways the hypothalamus accomplishes this is by regulating the pituitary gland and interacting with it via its own hormones.
These hormones are transported to the pituitary gland, where they serve as a cue for the pituitary to start producing one or more of its hormones. The endocrine glands that the pituitary hormones are targeting are then stimulated to create their own hormones. These locally made hormones are what actually regulate your body.
OA symptoms frequently appear gradually and get worse with time. Signs and symptoms of OA include:
Depending on the illness and affected hormone, specific symptoms can vary. The location and size of a tumor also matter. Typical signs include:
Pituitary diseases are primarily brought on by non-cancerous pituitary tumors, which make your body produce too much or too little of a certain hormone.
Additionally typical causes of pituitary issues include:
Treatment is not necessary for many pituitary tumors. Treatment is based on the type of tumor, its size, and how deep into the brain it has spread. Age and general health are also factors that need to be taken into consideration.
Prolactin-secreting tumors (prolactinomas)
ACTH-producing tumors (Cushing syndrome)
Growth hormone-secreting tumors

Scitron is a Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), derived from human umbilical cords. Upon treatment, the cultured cells are injected intramuscularly or intravenously into the patient. The cells are characterized by low immunogenicity, making them very safe, tolerable, and free of side effects.
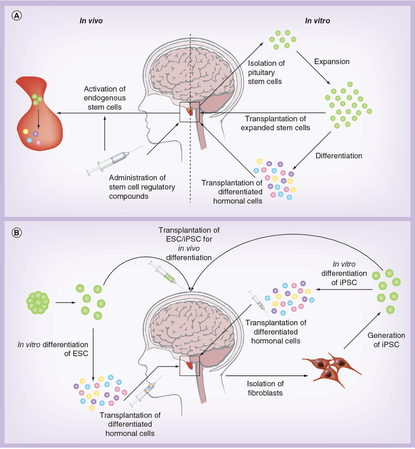
As shown in Figure (A), pituitary deficit can be corrected by inducing local stem cells in the pituitary to multiply and develop into the desired cell types. As an alternative, stem cells from pituitary tissue can be extracted, grown in a dish, and then either transplanted directly into the hypophysiotropic region beneath the hypothalamus or first differentiated and purified in a dish. The desired cell type can be created by transdifferentiating adult pituitary cells using the same methods.
As described in Figure B, Pluripotent stem cells, such as Embryonic Stem Cells (ESC) and iPSC, may be injected into the hypophysiotropic region of a patient with hypopituitarism, where they can develop to replace the damaged endocrine cell type. However, due to their tremendous ability for proliferation, the potent ESC and iPSC may result in the development of tumors. To get around this issue, ESC and iPSC could be differentiated in vitro first, followed by the isolation of the desired hormonal cell type and transplantation of only the pure cell type.
If you believe that our treatment options may be able to improve your condition and enhance your quality of life, please contact us to schedule a complimentary consultation with one of our in-house clinical specialists. Our consultations are available in both Malay and English language.





Review your medical history & recent evaluations
Explore what your treatment package might look like
Answer any questions you have about us
Answer any questions you have about the therapies
Discuss practical next steps,
if you feel we can effectively treat you

Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified GMP Lab, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.



Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified cGMP laboratory, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.


Proudly powered by CTG © 2010-2026 Cell Tissue Group, a Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Spin-Off Company. – All Rights Reserved.