- HOME
- ABOUT
- RESEARCH
- INSIGHTS & HAPPENINGS
- JOIN US
- CONTACT US
-

Macular Degeneration: Macular degeneration is a medical illness that causes blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field.

Macular degeneration, also known as Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a progressive loss of vision in the center of the visual field. In its early stages, there may be no signs of the condition. However, over time, some people may experience a gradual decline in eyesight, which can affect one or both eyes. While it does not lead to total blindness, loss of central vision can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks such as recognizing faces, driving, reading, etc. Visual hallucinations may also occur, but they do not indicate a mental condition.
Macular degeneration is more common in older adults. Risk factors include smoking and genetic factors. It is caused by damage to the retina’s macula. A comprehensive eye exam is used to make the diagnosis, and the severity is classified as early, middle, or late. The late stage is further divided into “dry” and “wet” forms, with the dry form accounting for 90% of case

The most common symptoms of age-related macular degeneration are as follows. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
One of the most typical early symptoms of age-related macular degeneration is the appearance of drusen, which are small yellow deposits in the retina. It could indicate that the eye is on the point of developing more serious age-related macular degeneration. During an eye exam, your doctor will be able to see these.
Age-related macular degeneration symptoms may resemble those of other eye disorders. Consult an eye care specialist for a diagnosis.

The macula, a region of the retina important for clear vision in the direct line of sight, is affected by dry macular degeneration. Over time, the tissue in the macula may shrink and lose vision-related cells. The exact cause of dry macular degeneration is not known, but research suggests that it may be influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors such as smoking, obesity, and diet. As the eye ages, the condition worsens.
The two primary types of age-related macular degeneration have different causes:
Dry: This is the most common type, affecting about 80% of people with AMD. Its exact cause is not known, but genetic and environmental factors are thought to be involved. Dry AMD is believed to be caused by age-related damage to a crucial support membrane beneath the retina.
Wet: This type is less common but usually results in more severe visual loss than dry AMD. Wet AMD is the leading cause of severe blindness. It develops when irregular blood vessels form beneath the retina, which can leak fluid and blood. As a result, wet AMD can cause a large blind spot in the centre of the visual field.
There is currently no cure for dry, age-related macular degeneration. However, vision treatment options and low-vision equipment can be used to improve visual abilities, learn new ways to do daily activities, and adapt to life with age-related macular degeneration.
The primary treatment for wet AMD is the injection of anti-VEGF medicines. VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) is a protein that promotes the growth of new blood vessels. High levels of VEGF in the eye have been linked to the formation of abnormal blood vessels, which cause much of the damage in wet AMD. Anti-VEGF medications are used to inhibit the growth of these abnormal blood vessels and restore vision in many patients.
Anti-VEGF injections have been shown to improve visual acuity in some patients. The drugs are delivered by injecting them directly into the affected eye. Although it may sound intimidating, patients are generally comfortable during the procedure as it is performed with a small needle and under the supervision of numbing (anesthetic) eye drops. Anti-VEGF treatment is often given on a regular basis and may require repeated injections to maintain the treatment effect. Your retinal doctor will discuss the optimal treatment regimen for you. Other therapies, such as laser therapy, may be used in certain patients if necessary.
CelltiX is a type of extracellular vesicle from Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) manufactured in a cGMP-compliant facility.
It is a novel form of a major paracrine factor released by MSCs into a culture medium, which plays an important role in a wide range of biological processes.
CelltiMax is a product derived from human umbilical cord-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). The cells are cultured, then administered to the patient via intramuscular or intravenous injection. They have the ability to differentiate into specialized cells with specific functions for various parts of the body, and can reduce inflammation, repair, renew, regenerate, and replace damaged cells.
Definition
Stem cells are unspecialized cells of the human body.
Extracellular vesicles, which is the medical term for tiny bubbles that are released from stem cells.
Function
Unique, can become any type of cell, and they act as both building blocks and repair mechanisms in your body.
Carry genetic information and proteins to cells throughout your body, and they create paths for communication between cells.
Origins
Donor stem cells are placed in your body and are guided into becoming specific cells in the body to replace and repair diseased cells.
Exosomes are extracted from donated human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and sterilized.
Growth Factors
Less amount of growth factors compared to exosomes.
Exosomes contain nearly three times the amount of growth factors. More growth factors mean a better ability to restore and revitalize target cells.
Administration
Accelerates healing
Reduced inflammation
Eliminates pain and inflammation
Supports metabolic function
Avoids the need for surgery
Improves brain health
Enhances collagen production
Reduces chronic pain
Decrease nerve damage
Enhances tissue regeneration
Less invasive procedure
Boost immune health
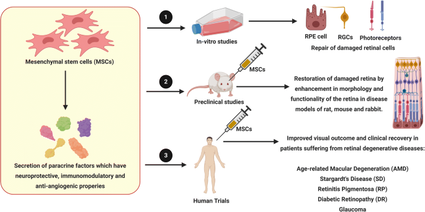
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) have been extensively researched for their potential in treating a variety of retinal diseases. Their therapeutic potential is due to their ability to differentiate into multiple lineages and secrete a variety of immunomodulatory, anti-angiogenic, and neurotrophic factors. Several studies have reported on the role of MSCs in retinal repair and regeneration, with MSC-secreted factors preventing retinal degeneration and improving retinal morphology and function.
MSCs also donate mitochondria to help retinal cells function, and exosomes secreted by MSCs have been shown to have anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties. Based on promising preclinical results, several clinical trials are being conducted to investigate the potential benefits of MSCs for the treatment of retinal diseases.
If you feel we might be able to offer meaningful improvement to both your condition and your quality of life, then please reach out to schedule a free consultation with one of our in-house clinical experts. We offer consultations in both Malay and English.





Review your medical history & recent evaluations
Explore what your treatment package might look like
Answer any questions you have about us
Answer any questions you have about the therapies
Discuss practical next steps,
if you feel we can effectively treat you

Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified GMP Lab, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.



Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified cGMP laboratory, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.


Proudly powered by CTG © 2010-2026 Cell Tissue Group, a Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Spin-Off Company. – All Rights Reserved.