- HOME
- ABOUT
- RESEARCH
- INSIGHTS & HAPPENINGS
- JOIN US
- CONTACT US
-

Diabetes mellitus: Diabetes is a common chronic illness, a type of metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia where levels of sugar in the blood are too high. Those with diabetes are also at risk of hypoglycaemia which is when the blood sugar level is too low.
Diabetes is mainly caused by insufficient secretion of insulin or resistance towards the insulin and is divided into three types: type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is known as insulin-dependent, as patients with this type of diabetes require daily insulin administration due to insufficient endogenous insulin as a result of autoimmune destruction on pancreatic β cells.
Type 2 diabetes is non-insulin dependent and is due to the body’s ineffective use of the insulin produced. This type of diabetes is mostly the result of being overweight, obesity, as well as lack of physical activity.
Gestational diabetes is caused by hyperglycemia in the blood glucose levels where the values exceed normal but are still insufficient to be diagnosed as diabetic and occurs during pregnancy.
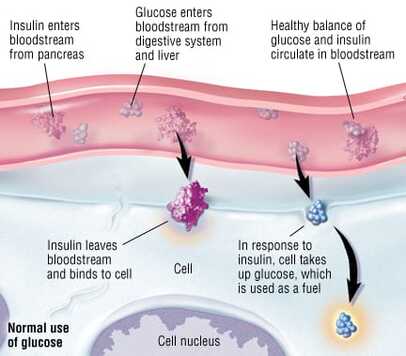
Normal physiology in non-diabetic individuals is characterized by the pancreas secreting digestive enzymes and hormones such as glucagon and insulin into the bloodstream to regulate glucose levels in the body. The release of insulin allows glucose to enter cells in the body, specifically muscle and liver cells, where it is then metabolized to produce energy. When the level of insulin is high, the liver stops its production of glucose and stores it in other forms until needed. When blood glucose levels are low, glucagon is secreted instead in order to promote the release of glucose stored in the liver.

Pathology of type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune reaction where the individual’s immune system destroys the pancreatic beta cells, which are the cells that produce insulin. Hence, the production of insulin is stopped.
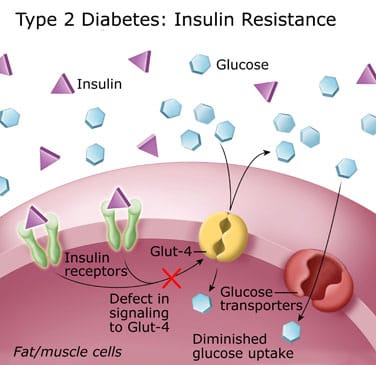
Pathology of type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes develops when either the body does not produce sufficient insulin or the cells ignore the insulin. This normally starts as insulin resistance. This disorder occurs when the cells do not use insulin properly, and as the need for insulin rises, the pancreas becomes unable to produce it, resulting in the accumulation of glucose in the blood instead.
• Insulin and Analogues
• Adequate lowering blood glucose
• Antioxidant
• Anti-inflammatory
• Anti-platelet
• Anti-hyperlipidemic
• Hypoglycaemia
• Requires continuous injection subcutaneously
• Requires regular monitoring
• Biguanides
• Adequate lowering blood glucose
• Less chance of hypoglycaemia
• Less cost
Risk of :
• lactic acidosis
• heart failure
• hepatic cirrhosis
• sepsis
• Sulfonylureas and glinides
• Adequate lowering blood glucose
• Less invasive as oral route is implemented
• Cardiovascular complications
• Hypoglycemia
• Sodium Glucose Co Transporter Inhibitor
• Moderate glucose lowering
• Less hypoglycemia
• Glycosuria
• UTI
• DPP-4 Inhibitor
• Moderate glucose lowering
• Increased hepatic glucose production
• Weight gain
• Hypoglycemia
• GLP-1 Agonist
• Adequate lowering blood glucose
• No hypoglycemia
• Weight loss
• GIT
• Pancreatic side effects
• Alpha-glucosidase Inhibitor
• Mild blood glucose lowering
• No hypglycemia
• Post-prandial hyperglycemia
• GIT problems
Scitron is a Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), derived from human umbilical cords. Upon treatment, the cultured cells are injected intramuscularly or intravenously into the patient. The cells are characterized by low immunogenicity, making them very safe, tolerable, and free of side effects.
CelltiMax is a product derived from human umbilical cord-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). The cells are cultured, then administered to the patient via intramuscular or intravenous injection. They have the ability to differentiate into specialized cells with specific functions for various parts of the body, and can reduce inflammation, repair, renew, regenerate, and replace damaged cells.
Stem Cell Research
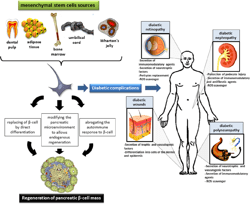
Type 1 diabetes
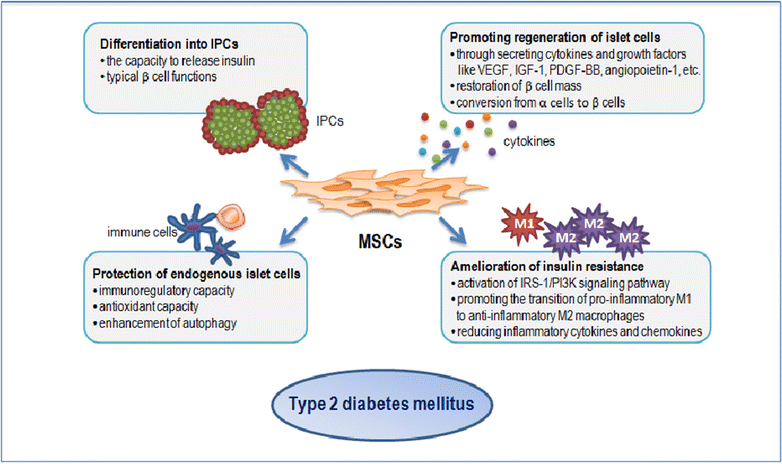
Type 2 diabetes
If you feel we might be able to offer meaningful improvement to both your condition and your quality of life, then please reach out to schedule a free consultation with one of our in-house clinical experts. We offer consultations in both Malay and English.





Review your medical history & recent evaluations
Explore what your treatment package might look like
Answer any questions you have about us
Answer any questions you have about the therapies
Discuss practical next steps,
if you feel we can effectively treat you

Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified GMP Lab, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.



Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified cGMP laboratory, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.


Proudly powered by CTG © 2010-2026 Cell Tissue Group, a Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Spin-Off Company. – All Rights Reserved.