- Potentially Treatable Condition
- Nervous System
- Neuronal Damage
- HOME
- ABOUT
- RESEARCH
- INSIGHTS & HAPPENINGS
- JOIN US
- CONTACT US
-

The term “brain damage” refers to injury to the brain brought on by a variety of circumstances, including head trauma, insufficient oxygenation, infections, or cerebral haemorrhage. A behavioural or functional anomaly could be connected to this harm.
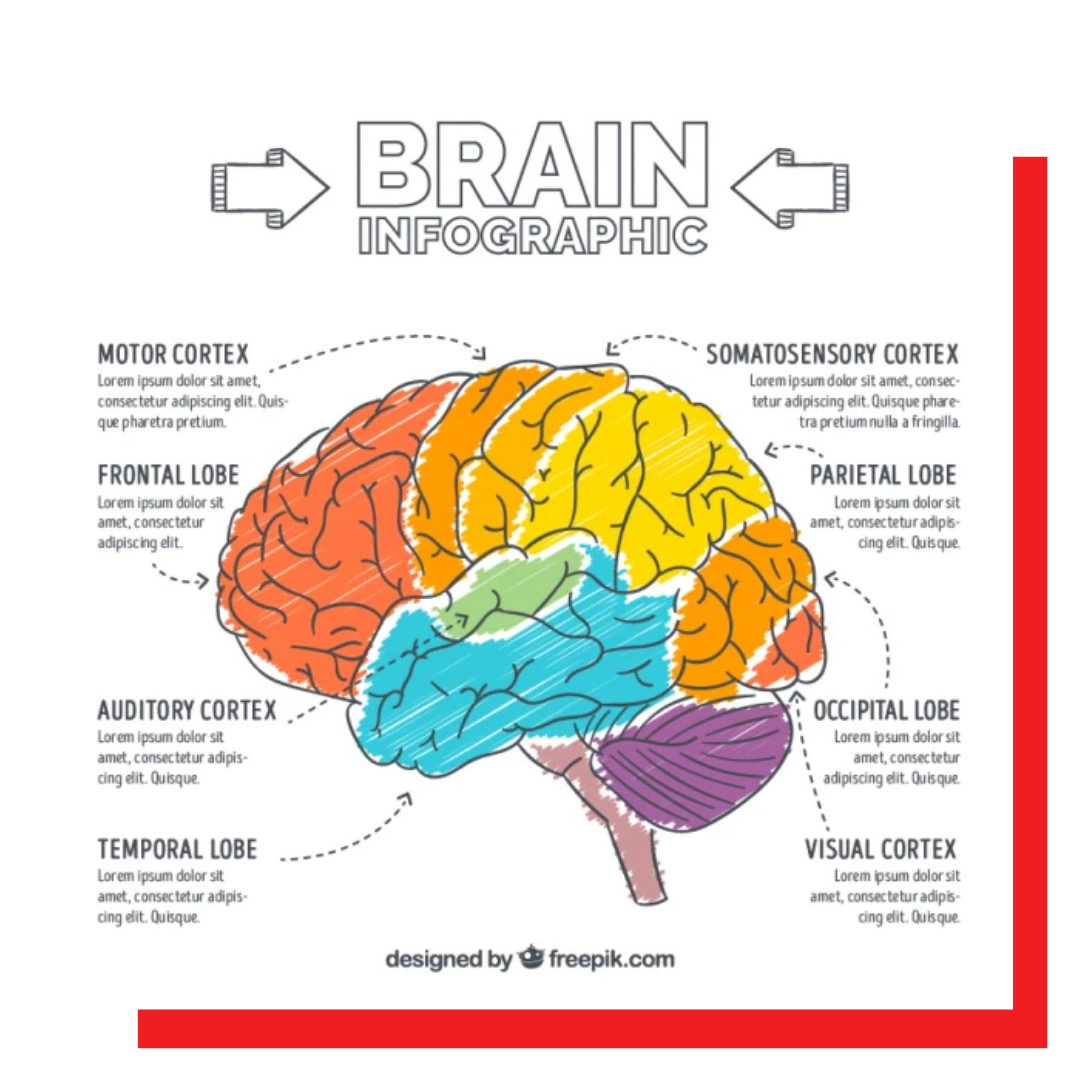
Neurotrauma, brain damage, or brain injury are terms used to describe the loss or degeneration of brain cells (BI). There are numerous internal and external factors that might harm the brain. The phrase “brain injury” generally refers to severe, consistent trauma-related damage.
Neurons are vulnerable to tearing, cutting, and pressure because they are fragile. A damaged neuron can stop impulses from entering and exiting the brain, affecting muscle control or causing numbness in the affected area. Nerve damage can have an impact on the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
Traumatic brain injury and acquired brain injury are the two different types of brain damage. Both interfere with the brain’s regular operations.
Physical symptoms
Sensory symptoms
Behavioural, cognitive, or mental symptoms
Physical symptoms
Behavioural, cognitive, or mental symptoms
Improve bodies’ natural healing abilities
High stabililty
Modulate the immune system
Low toxicity and immunogenicity
Locate and reduce areas of inflammation
High penetration
Replace damaged and diseased cells
Enhanced delivery efficiency
Causes of traumatic brain injury include:
Causes of acquired brain injury include:
Surgery
Surgical intervention to prevent further brain damage, such as
Medications
Rehabilitation therapies
CelltiX is a type of extracellular vesicle from Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) manufactured in a cGMP-compliant facility.
It is a novel form of a major paracrine factor released by MSCs into a culture medium, which plays an important role in a wide range of biological processes.
CelltiMax is a product derived from human umbilical cord-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). The cells are cultured, then administered to the patient via intramuscular or intravenous injection. They have the ability to differentiate into specialized cells with specific functions for various parts of the body, and can reduce inflammation, repair, renew, regenerate, and replace damaged cells.
Definition
Stem cells are unspecialized cells of the human body.
Extracellular vesicles, which is the medical term for tiny bubbles that are released from stem cells.
Function
Unique, can become any type of cell, and they act as both building blocks and repair mechanisms in your body.
Carry genetic information and proteins to cells throughout your body, and they create paths for communication between cells.
Origins
Donor stem cells are placed in your body and are guided into becoming specific cells in the body to replace and repair diseased cells.
Exosomes are extracted from donated human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and sterilized.
Growth Factors
Less amount of growth factors compared to exosomes.
Exosomes contain nearly three times the amount of growth factors. More growth factors mean a better ability to restore and revitalize target cells
Administration
Improve bodies’ natural healing abilities
High stabililty
Modulate the immune system
Low toxicity and immunogenicity
Locate and reduce areas of inflammation
High penetration
Replace damaged and diseased cells
Enhanced delivery efficiency

Stem cell research
Numerous preclinical studies show that the use of MSC in several experimental models of TBI (traumatic brain injury) can handle various disease pathology characteristics. TBI-induced motor and cognitive impairments in mice were reduced when MSCs were injected directly into the damaged brain or administered by IV or IA.
According to the experimental results, administering MSC research TBI rats and mice stimulated the wounded brain to produce trophic factors that supported neurogenesis, neuroprotection, and neural healing. MSC treatments are better at controlling inflammation. In the brains of TBI rats, Lin and colleagues showed that MSC implantation decreased proinflammatory genes and increased anti-inflammatory genes.
Exosome research
Exosomes released from MSCs appear to have a similar effect to their counterparts, according to recent research. MSC exosome intravenous infusion dramatically reduces motor impairments and enhances spatial memory in TBI rats by encouraging endogenous neurogenesis and angiogenesis.
Recent research has demonstrated that the secretome of IV-infused MSCs can reduce neuroinflammation by restricting the release of proinflammatory cytokines, controlling microglia polarisation, and reducing neural cell death. In a different study, MSC-derived exosomes in TBI rats reduced neuronal damage and aided functional recovery following brain insulation by preventing microglia proinflammatory activation.
If you feel we might be able to offer meaningful improvement to both your condition and your quality of life, then please reach out to schedule a free consultation with one of our in-house clinical experts. We offer consultations in both Malay and English.





Review your medical history & recent evaluations
Explore what your treatment package might look like
Answer any questions you have about us
Answer any questions you have about the therapies
Discuss practical next steps,
if you feel we can effectively treat you

Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified GMP Lab, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.



Founded in 2010, Cell Tissue Group is a pioneering Malaysian medical technology company and a spin-off from the National University of Malaysia (UKM). As Malaysia’s first Tissue Engineering firm, Cell Tissue Group operates within a certified cGMP laboratory, ensuring the highest standards of medical research and product development, particularly in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.


Proudly powered by CTG © 2010-2026 Cell Tissue Group, a Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Spin-Off Company. – All Rights Reserved.